在项目开发过程中需要将字符串转化成为16进制的字符串,在网上找到了一些方法尝试之后,均发现存在一个问题–>字符串转为16进制后再转回来,英文正常,中文出现乱码
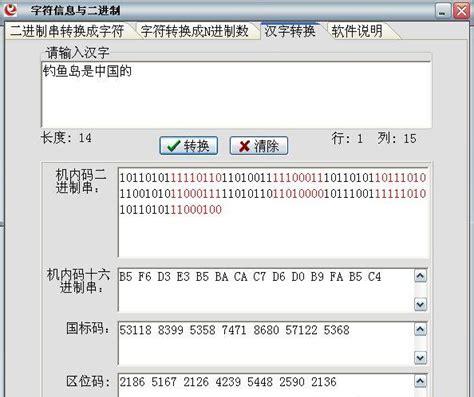
经过考虑决定通过以下方式进行解决:
1)在将字符串转为16进制之前先进行一次转化,先将其转化成为Unicode编码(相当于把中文用英文字符代替),在转化成为16进制
2)相反的,在十六进制转换为字符串后的得到的是Unicode编码,此时再将Unicode编码解码即可获取原始字符串
代码如下:
字符串转换unicode
/** * 字符串转换unicode */public static String string2Unicode(String string) { StringBuffer unicode = new StringBuffer(); for (int i = 0; i < string.length(); i ) { // 取出每一个字符 char c = string.charAt(i); // 转换为unicode unicode.append(“\\u” Integer.toHexString(c)); } return unicode.toString();}
字符串转16进制
/** * 字符串转化成为16进制字符串 * @param s * @return */public static String strTo16(String s) { String str = “”; for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i ) { int ch = (int) s.charAt(i); String s4 = Integer.toHexString(ch); str = str s4; } return str;}
*16进制转为字符串
/** * 16进制转换成为string类型字符串 * @param s * @return */public static String hexStringToString(String s) { if (s == null || s.equals(“”)) { return null; } s = s.replace(” “, “”); byte[] baKeyword = new byte[s.length() / 2]; for (int i = 0; i < baKeyword.length; i ) { try { baKeyword[i] = (byte) (0xff & Integer.parseInt(s.substring(i * 2, i * 2 2), 16)); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } try { s = new String(baKeyword, “UTF-8”); new String(); } catch (Exception e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } return s;}
*Unicode转为字符串
/** * unicode 转字符串 */public static String unicode2String(String unicode) { StringBuffer string = new StringBuffer(); String[] hex = unicode.split(“\\\\u”); for (int i = 1; i < hex.length; i ) { // 转换出每一个代码点 int data = Integer.parseInt(hex[i], 16); // 追加成string string.append((char) data); } return string.toString();}
此方法虽然解决了转化过程中中文乱码的问题,但是过于复杂,笔者后来又发现一种新的转化方式,可直接转化,中文不乱码。
代码如下:
*字符串转16进制
/** * 字符串转换成为16进制(无需Unicode编码) * @param str * @return */public static String str2HexStr(String str) { char[] chars = “0123456789ABCDEF”.toCharArray(); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(“”); byte[] bs = str.getBytes(); int bit; for (int i = 0; i < bs.length; i ) { bit = (bs[i] & 0x0f0) >> 4; sb.append(chars[bit]); bit = bs[i] & 0x0f; sb.append(chars[bit]); // sb.append(‘ ‘); } return sb.toString().trim();}
*16进制转为字符串
/** * 16进制直接转换成为字符串(无需Unicode解码) * @param hexStr * @return */public static String hexStr2Str(String hexStr) { String str = “0123456789ABCDEF”; char[] hexs = hexStr.toCharArray(); byte[] bytes = new byte[hexStr.length() / 2]; int n; for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i ) { n = str.indexOf(hexs[2 * i]) * 16; n = str.indexOf(hexs[2 * i 1]); bytes[i] = (byte) (n & 0xff); } return new String(bytes);}
扩展:
将指定byte数组以16进制的形式打印到控制台
package com.nantian.iclient.atm.sdb; public class Util { public Util() { } /** * 将指定byte数组以16进制的形式打印到控制台 * @param hint String * @param b byte[] * @return void */ public static void printHexString(String hint, byte[] b) { System.out.print(hint); for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i ) { String hex = Integer.toHexString(b[i] & 0xFF); if (hex.length() == 1) { hex = ‘0’ hex; } System.out.print(hex.toUpperCase() ” “); } System.out.println(“”); } /** * * @param b byte[] * @return String */ public static String Bytes2HexString(byte[] b) { String ret = “”; for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i ) { String hex = Integer.toHexString(b[i] & 0xFF); if (hex.length() == 1) { hex = ‘0’ hex; } ret = hex.toUpperCase(); } return ret; } /** * 将两个ASCII字符合成一个字节; * 如:”EF”–> 0xEF * @param src0 byte * @param src1 byte * @return byte */ public static byte uniteBytes(byte src0, byte src1) { byte _b0 = Byte.decode(“0x” new String(new byte[]{src0})).byteValue(); _b0 = (byte)(_b0 << 4); byte _b1 = Byte.decode(“0x” new String(new byte[]{src1})).byteValue(); byte ret = (byte)(_b0 ^ _b1); return ret; } /** * 将指定字符串src,以每两个字符分割转换为16进制形式 * 如:”2B44EFD9″ –> byte[]{0x2B, 0x44, 0xEF, 0xD9} * @param src String * @return byte[] */ public static byte[] HexString2Bytes(String src){ byte[] ret = new byte[8]; byte[] tmp = src.getBytes(); for(int i=0; i<8; i ){ ret[i] = uniteBytes(tmp[i*2], tmp[i*2 1]); } return ret; } }